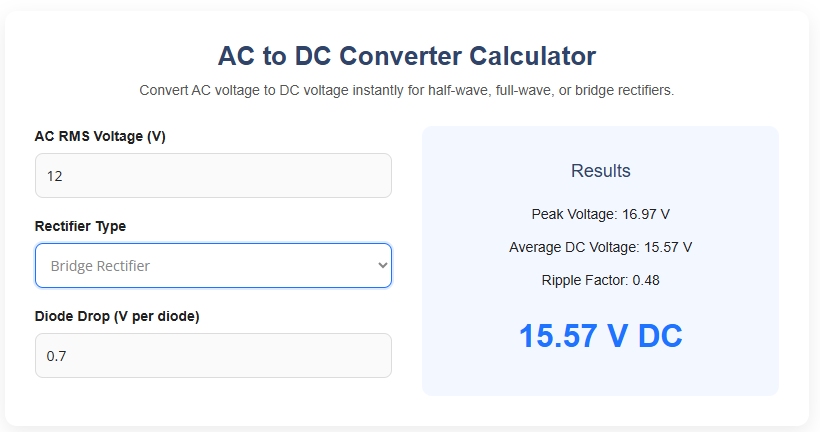
AC to DC Converter Calculator
Convert AC voltage to DC voltage instantly for half-wave, full-wave, or bridge rectifiers.
Results
AC to DC Converter Calculator
An AC to DC Converter Calculator is an online tool that helps you convert alternating current (AC) voltage into direct current (DC) voltage quickly and accurately. It is especially useful for students, electricians, electronics hobbyists, and engineers who work with rectifiers, power supplies, and electronic circuits.
Instead of doing manual calculations for peak voltage, average DC output, and losses due to diodes, this calculator gives instant results based on standard electrical formulas.
What Is AC to DC Conversion?
AC voltage continuously changes its direction and magnitude, while DC voltage flows in a single direction with a steady polarity. Most electronic devices, such as mobile phones, laptops, LEDs, and microcontrollers, require DC power.
To make AC usable for electronics, it is passed through a rectifier circuit that converts AC into pulsating DC. This output can later be filtered and regulated for smoother DC.
What Does an AC to DC Converter Calculator Do?
The AC to DC Converter Calculator takes your input values and calculates:
- Peak voltage after conversion
- Average DC output voltage
- Effect of diode voltage drop
- Ripple characteristics based on rectifier type
This saves time and avoids calculation errors, especially when comparing different rectifier configurations.
Inputs Used in the Calculator
1. AC RMS Voltage (V)
This is the RMS value of the AC supply voltage, such as 12 V or 230 V. RMS voltage represents the effective value of AC power.
2. Rectifier Type
You can select the rectifier circuit used for conversion:
- Half-wave rectifier
- Full-wave rectifier
- Bridge rectifier
Each rectifier has a different efficiency and voltage drop.
3. Diode Drop (V per diode)
A diode does not conduct without loss. Common silicon diodes have a forward drop of about 0.7 V. The total drop depends on how many diodes conduct in the rectifier circuit.
AC to DC Conversion Formula
First, the peak voltage is calculated from the RMS voltage:
\(\text{Peak Voltage (Vp)} = V_{rms} \times \sqrt{2}\)Then, diode drops are subtracted based on rectifier type:
- Bridge rectifier: subtract voltage drop of two diodes
- Full-wave rectifier (center-tapped): subtract one diode drop
- Half-wave rectifier: subtract one diode drop
For a bridge rectifier, average DC voltage is approximately:
\(\text{Vdc} = (V_{rms} \times \sqrt{2}) – (2 \times V_d)\)Where:
- Vdc = average DC output voltage
- Vrms = AC RMS voltage
- Vd = diode forward voltage
Rectifier Types Explained
Half-Wave Rectifier
- Uses only one half of the AC cycle
- Simple but inefficient
- High ripple and low DC output
Full-Wave Rectifier
- Uses both halves of the AC cycle
- Better efficiency than half-wave
- Requires a center-tapped transformer
Bridge Rectifier
- Most commonly used
- Uses four diodes
- No center-tapped transformer required
- Higher DC output and better performance
Why Use an AC to DC Converter Calculator?
- Instant and accurate results
- No manual formula application
- Ideal for learning and practical design
- Helpful in power supply planning
- Reduces calculation mistakes
This tool is useful for academic problems, electronics projects, and real-world electrical applications.
Practical Example
If you enter:
- AC RMS Voltage: 12 V
- Rectifier Type: Bridge Rectifier
- Diode Drop: 0.7 V
The calculator will show:
- Peak voltage around 16.97 V
- Average DC voltage around 15.57 V
This helps you decide if the output is suitable for your circuit.
Applications of AC to DC Conversion
- Power adapters and chargers
- DC motor drives
- LED power supplies
- Battery charging circuits
- Electronic control systems
Student-Friendly Steps: Convert 12V AC to 12V DC
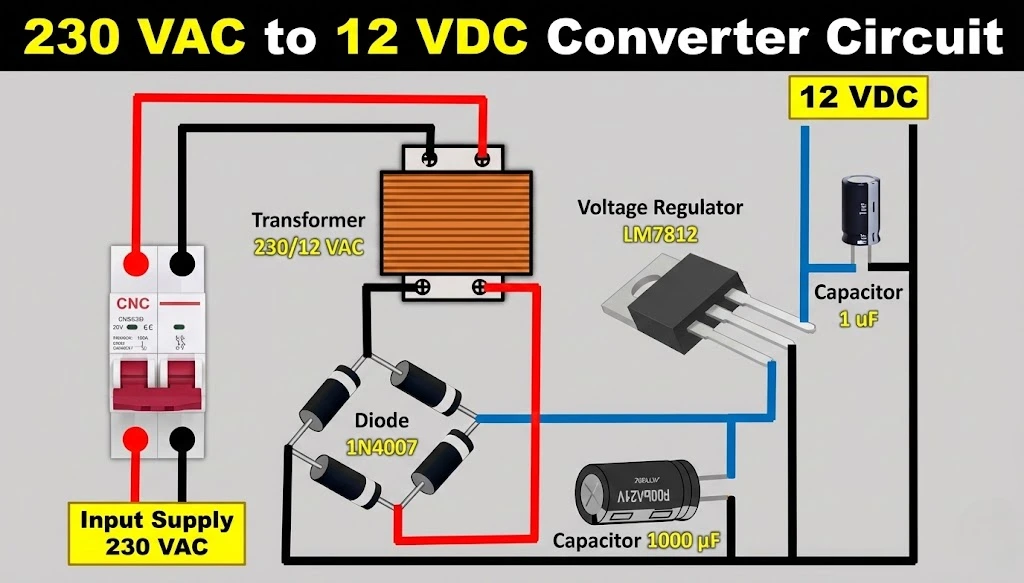
Step 1: Rectify the AC (AC → Pulsating DC)
- Take 12V AC input.
- Pass it through a bridge rectifier (4 diodes).
- Diodes allow current to flow in only one direction.
- Output becomes pulsating DC.
Formula for peak voltage:
\(\text{Vpeak} = V_{AC} \times \sqrt{2}\)
Example:
\(\text{Vpeak} = 12 \times \sqrt{2} = 16.97V\)
After diode drop (≈1.4V for bridge rectifier), usable DC is about 15.5V.
Step 2: Smooth the DC (Remove Ripples)
- Connect a large capacitor after the rectifier.
- Capacitor stores charge and fills gaps between pulses.
- Output becomes smooth DC, but voltage still changes slightly.
Step 3: Regulate the Voltage (Fix at 12V DC)
- Use LM7812 voltage regulator.
- It converts fluctuating DC into a steady 12V DC.
- Small capacitors are added at input and output for stability.
Step 4: Get Final 12V DC Output
- Output is now:
- Stable
- Safe
- Ready for electronic circuits
Component Value Table (12V AC to 12V DC)
| Component | Typical Value | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| Transformer | 230V AC → 12V AC | Steps down mains voltage |
| Diodes | 1N4007 (4 pcs) | Rectification |
| Bridge Rectifier | 1A / 1000V | Converts AC to DC |
| Filter Capacitor | 1000µF – 2200µF / 25V | Reduces ripple |
| Regulator IC | LM7812 | Fixed 12V output |
| Input Capacitor | 0.33µF | Regulator stability |
| Output Capacitor | 0.1µF – 1µF | Noise reduction |
| Heat Sink | As required | Prevents regulator overheating |
What Is Ripple Factor? (Easy Explanation)
Ripple means small ups and downs in DC voltage after rectification.
Ripple Factor tells how smooth or rough the DC is.
Formula:
\(\text{Ripple Factor} = \frac{\text{AC component}}{\text{DC component}}\)
Ripple Comparison
| Rectifier Type | Ripple Factor |
|---|---|
| Half-wave | 1.21 (very high ripple) |
| Full-wave | 0.48 |
| Bridge Rectifier | 0.48 |
| With Capacitor Filter | Very low |
Lower ripple factor = better DC quality.
Voltage Losses Explained Simply
1. Diode Loss
- Each silicon diode drops about 0.7V
- Bridge rectifier uses 2 diodes at a time
- Total loss:
\(\text{Diode Loss} = 2 \times 0.7 = 1.4V\)
2. Regulator Loss (Heat Loss)
- LM7812 converts extra voltage into heat
- Power loss formula:
\(\text{Power Loss} = (V_{in} – 12) \times I\)
Example:
\(\text{Power Loss} = (15.5 – 12) \times 1A = 3.5W\)
That is why a heat sink is needed.
3. Transformer Loss
- Small loss due to copper resistance and core heating
- Usually ignored in basic calculations
Final Summary (For Exams)
- AC is converted to DC using rectifier + filter + regulator
- Capacitor reduces ripple
- LM7812 gives fixed 12V DC
- Ripple factor shows DC smoothness
- Voltage losses mainly come from diodes and regulator
FAQs
How do you calculate AC to DC converter?
To calculate AC to DC voltage, first convert the AC RMS voltage into peak voltage. The basic formula used is:
\(\text{Vpeak} = V_{AC} \times \sqrt{2}\)After finding the peak voltage, subtract the diode voltage drop based on the rectifier type. For a bridge rectifier, subtract the drop of two diodes.
Example:
If AC voltage = 120 V
After diode drops, the DC voltage will be slightly lower.
How do you convert AC to DC voltage?
AC is converted to DC using a rectifier circuit. The steps are:
1. Apply AC voltage to a rectifier (half-wave, full-wave, or bridge).
2. Rectifier converts AC into pulsating DC.
3. Diodes cause a small voltage drop.
4. Filters and regulators can smooth the DC output.
An AC to DC Converter Calculator performs these steps automatically.
How to convert 220V AC to DC?
To convert 220V AC to DC:
Use a bridge rectifier.
Calculate peak voltage:
Subtract diode drops (about 1.4 V for bridge rectifier).
Add filtering and regulation to get stable DC.
How to calculate AC to DC ratio?
The AC to DC ratio compares RMS AC voltage to average DC voltage. For a full-wave rectifier, the approximate ratio is:
\(\text{AC to DC Ratio} \approx 1.11\)This ratio varies depending on rectifier type and filtering.
What is RMS voltage in AC?
RMS voltage is the effective value of AC voltage that delivers the same power as DC voltage of the same value.
Which rectifier is best for power supplies?
Bridge rectifiers are commonly preferred due to better efficiency and transformer simplicity.
Is filtering included in this calculator?
This calculator focuses on rectification. Filtering and regulation are usually handled by capacitors and voltage regulators.
Why does DC voltage come out lower than peak voltage?
Voltage drops across diodes and losses in the rectifier reduce the final DC output.
Conclusion
An AC to DC Converter Calculator is a simple yet powerful tool for understanding and designing rectifier-based power supplies. By entering basic electrical values, you can instantly find DC output voltage, peak values, and losses. It is ideal for students, professionals, and anyone working with electrical or electronic systems.